ESMS, ICMS
Engineering systems monitoring system, industrial industrial complexes monitoring system (ESMS)
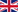
 ESMS is built on the basis of software and hardware and is designed to monitor the technological processes and processes to ensure the operation of equipment directly at potentially hazardous facilities, in buildings and structures and transfer information about their condition through communication channels to the duty and dispatch services of these facilities for further processing with the purpose of assessing, preventing and eliminating the consequences of destabilizing factors in real time, as well as for conveying information about the forecast and the fact in the emergence of emergencies, including those caused by terrorist acts, to the Crisis Management Center (CMC) and the Unified Dispatch Control Service (UDCS) of the municipal formation.
ESMS is built on the basis of software and hardware and is designed to monitor the technological processes and processes to ensure the operation of equipment directly at potentially hazardous facilities, in buildings and structures and transfer information about their condition through communication channels to the duty and dispatch services of these facilities for further processing with the purpose of assessing, preventing and eliminating the consequences of destabilizing factors in real time, as well as for conveying information about the forecast and the fact in the emergence of emergencies, including those caused by terrorist acts, to the Crisis Management Center (CMC) and the Unified Dispatch Control Service (UDCS) of the municipal formation.
The list of objects for which it is necessary to develop the MISC:
In accordance with clause 4.9 GOST R 22.1.12-2005 (herefrom 01-07-2011 SMIS are subject to mandatory installation on the following categories of objects:inafter GOST for SMI) with amend.
- facilities where:
- dangerous substances are produced, used, processed, formed, stored, transported, destroyed in quantities exceeding the limits established by the legislation of the Russian Federation;
- destruction, burial of chemical and other hazardous waste;
- there are large warehouses for storage of oil and oil products (over 20,000 tons) and isothermal storage of liquefied gases.
- communication facilities that are particularly dangerous, technically complex in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation in the field of communications;
- power transmission lines and other electric grid facilities with a voltage of 330 kilovolts or more;
- airports and objects of their infrastructure;
- objects of public transport infrastructure;
- subways;
- facilities for the development of oil fields on the shelves of the seas;
- main gas-oil and product pipelines;
- objects of gas distribution systems on which natural gas or liquefied hydrocarbon gas is used, stored, transported;
- hydraulic structures of the 1st, 2nd and 3rd grades;
- large industrial facilities, with the number of employed people more than 10 thousand people;
- objects of capital construction, in the design documentation of which at least one of the following characteristics is provided:
- height more than 100 meters;
- spans over 100 meters;
- the presence of a console more than 20 meters.
- objects with a maximum estimated stay of 500 people or more: entertainment, sports facilities, multifunctional office and shopping and entertainment complexes, health facilities, hotels;
- life support facilities: installations, warehouses, storage facilities, hydraulic engineering and engineering protective structures, communications, destruction (damage) which can lead to disruption of normal life activity of people (cessation of water, gas, heat, electricity, flooding, damage to residential areas, failure of systems sewerage and wastewater treatment) and as a result - an emergency.
- and others in accordance with GOST R 22.1.12-2005.
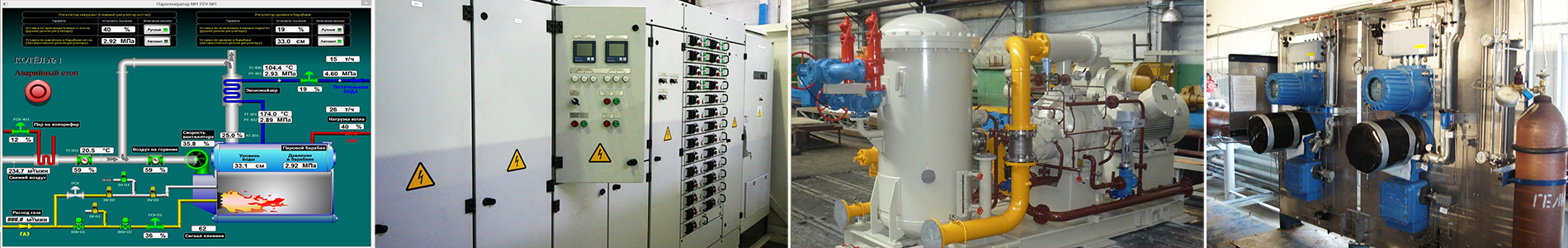
The equipment of especially dangerous objects of ESMS should be carried out at carrying out:
- design, construction and installation works - for newly constructed facilities;
- planned overhaul - for objects in operation.
The commissioning of the above facilities, without the equipment of their SMIS, is not allowed.
It should also be noted that in accordance with clause 5.10 of GOST R 22.112-2005, the SMI should be developed as part of the section (subsection) of the project documentation "List of Civil Defense Measures, Measures for Prevention of Emergencies of Natural and Technogenic Character".
The main functions of the ESMS:
- forecasting and prevention of emergency situations;
- collection, transmission and processing of information about the parameters of the processes of the object;
- transmission of emergency reports on the site to the PSAP;
- launching of the emergency notification system;
- launching of an emergency prevention / elimination system;
- documentation and registration.
The choosing of the ESMS structure is based on the degree of automation of the object. Considering that mainly petrochemical facilities have a high degree of automation, the choice often comes from the integrated structure of the ESMS.
One of the components of the ESMS system is the monitoring system of engineering (bearing) structures (ESMS).
Appointment of ESMS:
- timely notification of a critical change in the state of the bearing structures of the complex and ensuring the adoption of reasonable decisions to ensure the safety of visitors and personnel, safe operation; termination of operation;
- monitoring and registration during the whole period of operation of changes in the state of load-bearing structures due to the accumulation of operational defects in them, which over time can lead a building, construction into a critical condition requiring appropriate repair or termination of operation.
The aims of the ESMS system are:
- ensuring the safety of personnel, visitors by automatic, real-time monitoring of the integral characteristics of the stress-strain state of load-bearing structures, timely informing the duty and dispatching service of the building, construction and PSAP of the city and the district about their critical change;
- reducing the risk of loss of structural properties of the structure, determining its reliability through the timely detection at an early stage of a negative change in the state (stress-strain state) of load-bearing structures, which can lead to their destruction and entail human losses, the transition of a building, a structure to a limited operational capacity, to a complete or partial loss of bearing capacity.
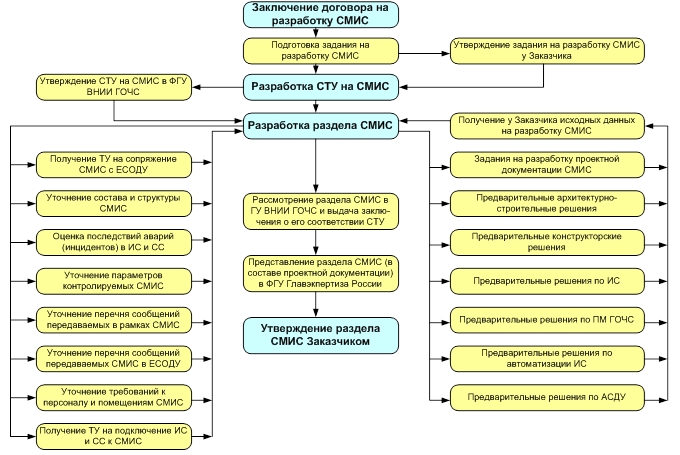
The ESMS includes:
- servers, local servers and ESMS controllers;
- AWP ESMS;
- equipment for data collection and transmission networks;
- sensors for monitoring the change in the state of bases, building structures of buildings and structures; engineering protection structures, as well as plots of possible mudslides, landslides, avalanches.